CARBON DIOXIDE
CAPTURE, TREATMENT,
STORAGE AND USE (CCUS)
Carbon capture, use and storage, or CCUS (Carbon capture, use and storage) are important emission reduction technologies that can be applied throughout the energy system. The use of CCUS system in power generation projects not only minimizes the carbon footprint, but also generates additional profit on sales of recycled CO2. MKC Group of Companies offers turnkey design and construction of zero-emission CO2 gensets and integrated implementation of CCUS technologies at energy facilities.
WORLD-
CHANGING
TECHNOLOGIES
The technological solution of MKC Group of Companies lies in the creation of an energy complex combined with associated chemical production. This will allow to process CO2 produced by the generator into chemical products in demand on the market (such as methanol, polymers, chemicals, etc.). This solution will significantly reduce emissions harmful to the environment and allow the development of additional chemical production, thus diversifying its business.
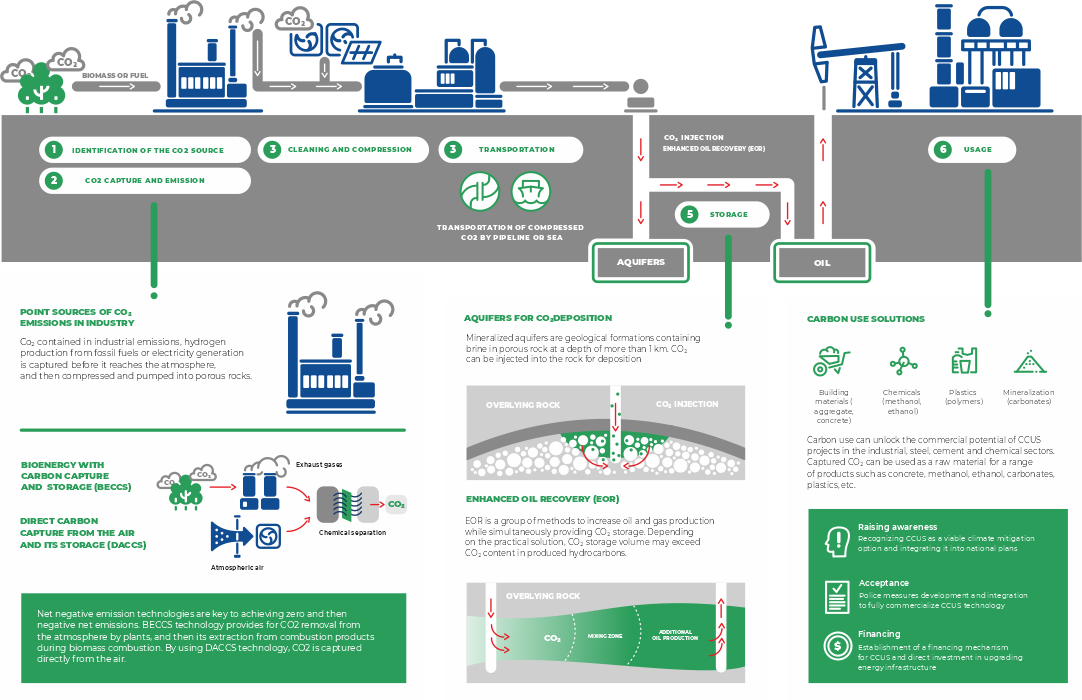
General technological scheme of CCUS projects:
The source for carbon dioxide production is a 2 MW capacity gas genset power plant
Coolant – genset exhaust flue gases
CCUS system capacity – 500 kg/h
Water consumption (after chemical water treatment) – at least 4 m3/h
Electric power consumption – 180 kW (specified during design)
Carbon dioxide module area - 12x24 m
External platform (cooling towers) – 18x6 m
Industrial voltage – 380/220 V, 50 Hz
The market for recycled CO2 has great potential. The main industry is chemical industry. The use of CCUS system in power generation projects not only minimizes the carbon footprint, but also generates additional profit on sales of recycled CO2. Carbon use can unlock the commercial potential of CCUS projects in the industrial, steel, cement and chemical sectors.
Fields of CO2 application


Today, there are 28 large industrial facilities in 10 countries where carbon dioxide is captured and used. They recycle a total of 40 million tons of CO2 per year. More than half of this volume comes from natural gas processing plants. The rest goes to the hydrogen, synthetic fuels, electricity, fertilizers, biofuels, as well as iron and steel industries. According to IEA forecasts, in the coming years, CO2 capture will begin everywhere — it will allow the world to reduce at least 15% of all greenhouse emissions in order to keep global warming within 2°C.